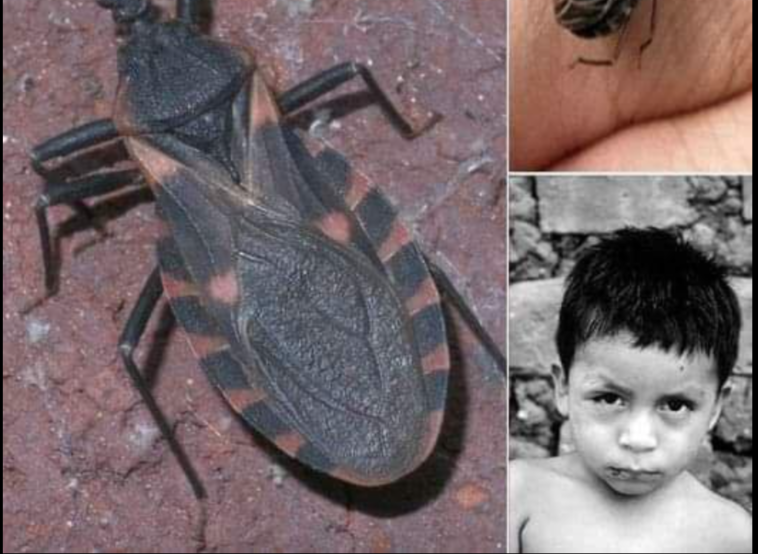
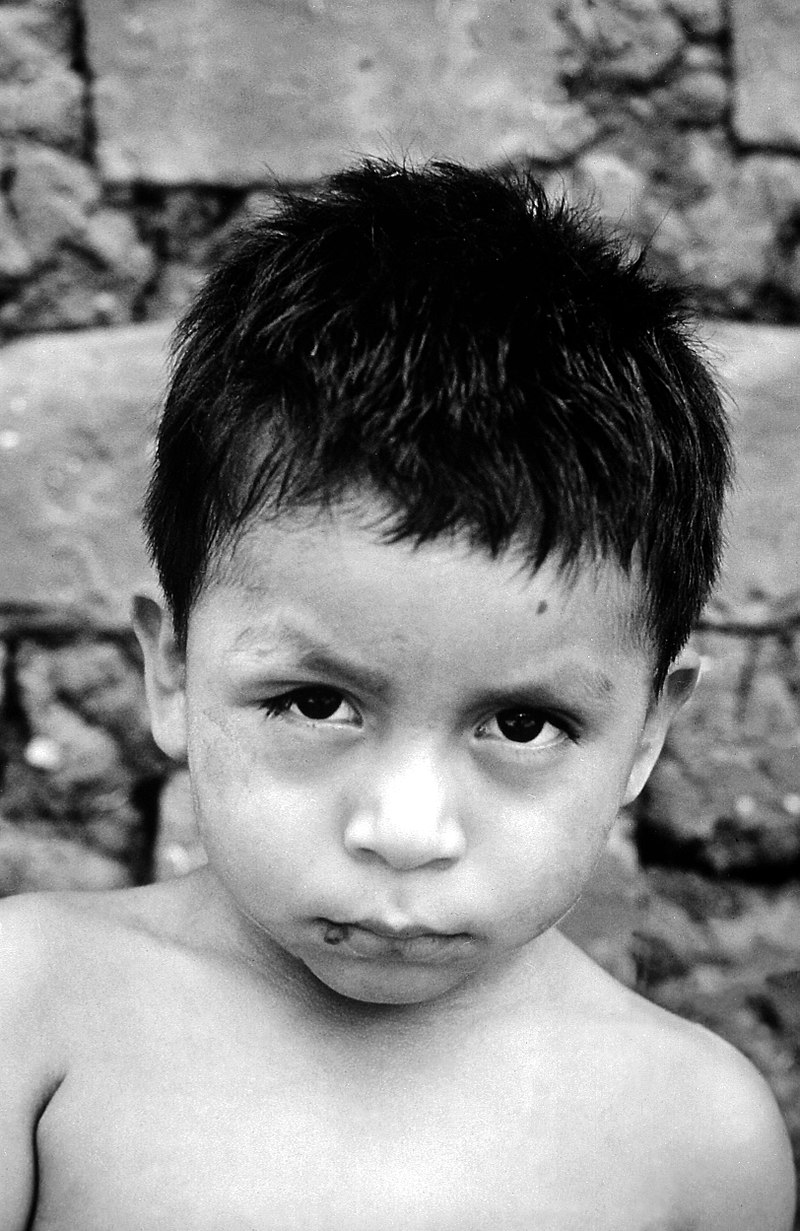
As a young child Emiliana Rodríguez recalls watching friends play a nighttime game of soccer, where one of the players suddenly dropped dead on the field. Not knowing what had happened, the Bolivian-born Rodríguez grew fearful of the night, afraid of the silent killer called Chagas, the “monster” she was told only comes out at night.
Chagas is a different kind of monster, a “silent and silenced disease,” transmitted by nocturnal bugs that infect up to 8 million people each year, and Rodríguez’ friend was one of 12,000 people killed each year.
Emiliana Rodríguez, 42, moved from Bolivia to Barcelona 27 years ago and realized she couldn’t escape Chagas, that she calls a “monster.”
“The fear usually came at night. Sometimes I didn’t sleep,” she said. “I was afraid of sleeping and not waking up.”
It was eight years ago when, pregnant with her first child, Rodríguez took some tests that revealed she was a carrier of Chagas. “I was paralysed with shock and remembered all those stories my relatives told me about people suddenly dying,” she said, also recalling the death of her friend. “I thought, ‘What’s going to happen to my baby?’”

But Rodríguez underwent treatment to prevent the parasite from reaching her unborn child through vertical transmission. After her baby girl was born, she tested negative.
Meanwhile, in Mexico, Elvira Idalia Hernández Cuevas had never heard of Chagas until her 18-year-old was diagnosed with the silent killer.
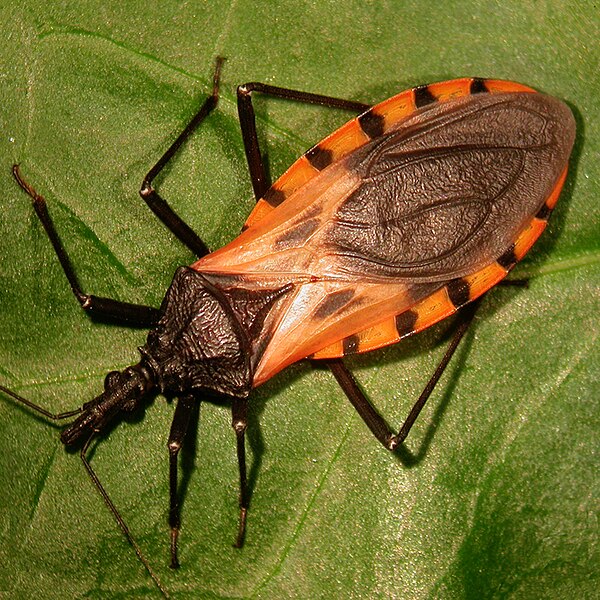
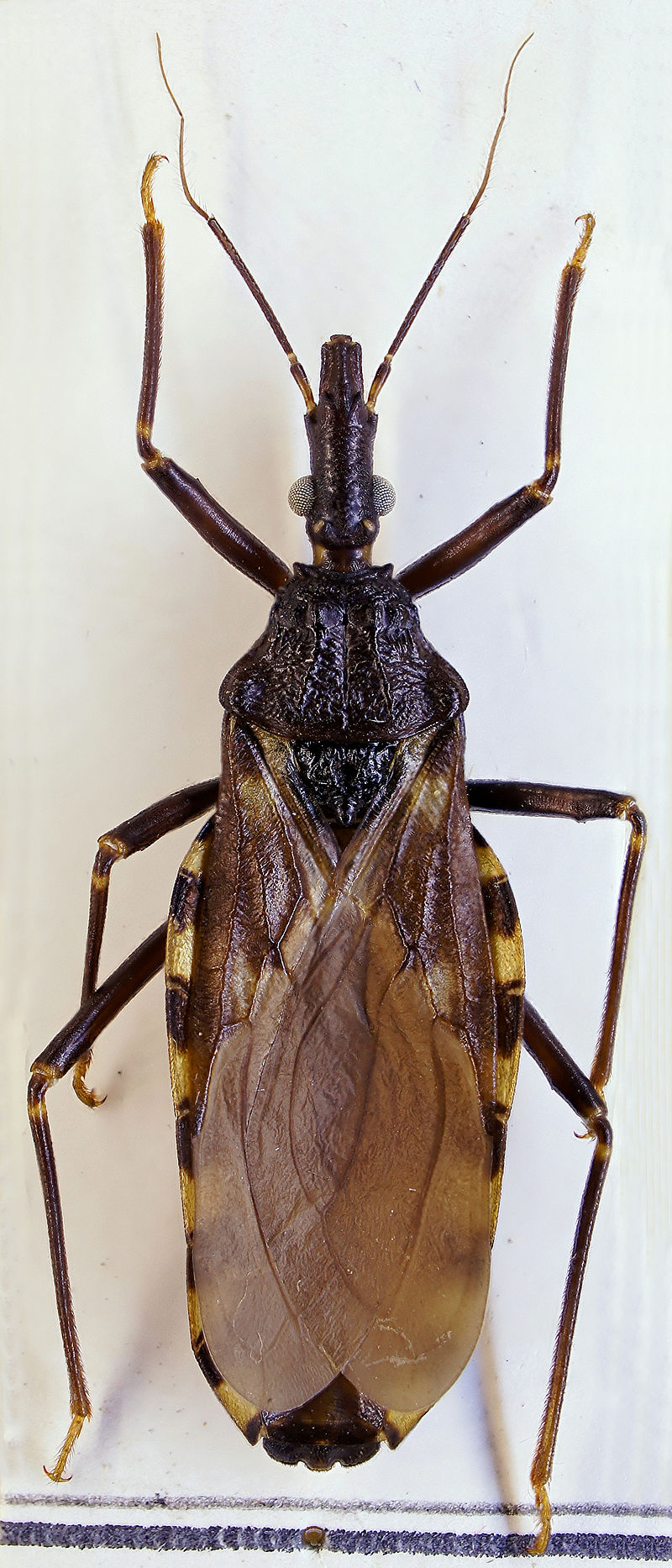
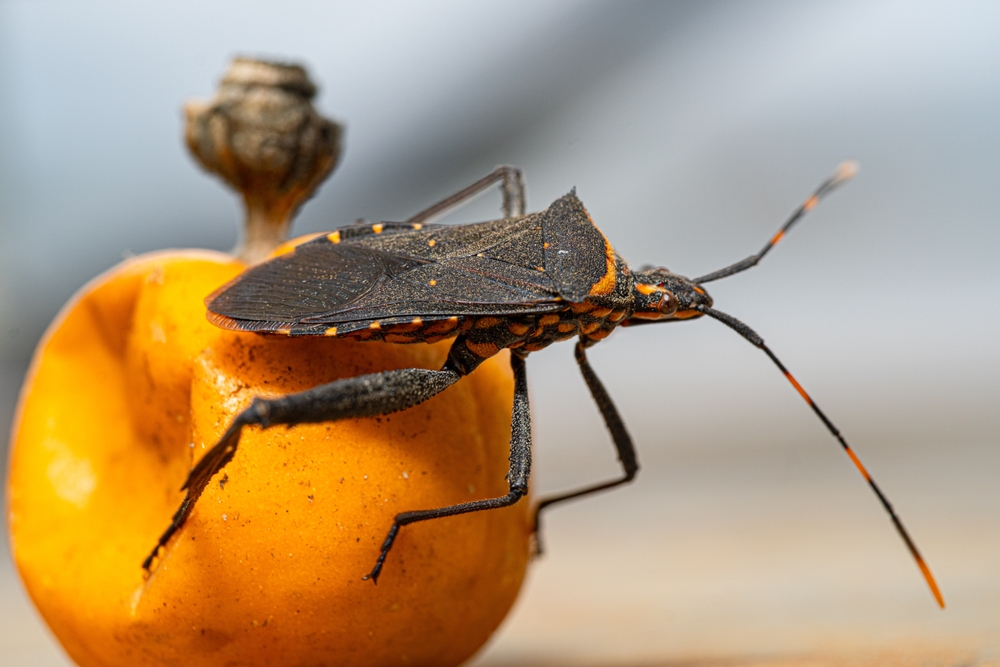
Idalia, 18, was donating blood in her hometown, near Veracruz in Mexico, when her sample was screened, resulting in a positive diagnosis for Chagas, a disease caused by a blood-sucking parasite, triatomine bugs that are commonly known as kissing or vampire bugs.
“I had never heard of Chagas so I started to research it on the internet,” Hernández said in an interview with the Guardian. “I was terrified when I saw it described as a silent killer. I didn’t know what to do or where to go.”
She’s not the only one, many people are unaware of the vectorborne illness caused by these pesky pests.
Chagas is named after Carlos Ribeiro Justiniano Chagas, a Brazilian physician and researcher who identified the human case in 1909. Over the past several decades, Chagas disease is known to be prevalent in Latin America, North America, Europe, Japan and Australia.

Kissing bugs mostly live in the walls of low-income housing in rural or suburban areas and are most active at nighttime when people are sleeping. The bug passes the T. cruzi infection by biting an animal or human, then defecating on the skin of its victim, who may accidentally scratch the spot and break the skin, or spread the feces into the eyes or mouth.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in Mexico, Central America, and South America, approximately 8 million people–6 to 7 million worldwide as reported by the World Health Organization (WHO)– have Chagas disease, the majority unaware of their infection. When left untreated, the lifelong infection can be a killer. About 12,000 people die of Chagas each year, killing “more people in Latin America than any other parasite disease, including malaria,” writes the Guardian.
Though these bugs have been identified in the U.S.–close to 300,000 people are infected–it is not considered an endemic.
Some people never develop symptoms but CDC reports that decades later, 20 to 30% have cardiac complications that can lead to death, or gastrointestinal complications, which can cause severe discomfort.
And the global case detection rate is only 10%, which makes treatment and prevention very difficult.

Looking for some support, Hernández and her daughter Idalia visited several doctors who also knew very little–if anything–about Chagas, or how to treat it. “I was surprised, scared and sad because I thought my daughter was going to die. Above all, I couldn’t find out any reliable information, and this added to my anxiety,” Hernández said.
Finally getting some help from a family member who worked in health care, Idalia received the treatment she needed.
“In Mexico, the authorities say that there aren’t many people affected by Chagas and that it’s under control, but that’s not the situation,” says Hernández. “Medical professionals don’t receive any training and mistake Chagas for other heart diseases. The majority don’t realize there is Chagas in Mexico.”
Chagas is listed by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a neglected tropical disease, meaning it’s not getting attention from the global health policy agenda.
Chagas disease treatment
Colin Forsyth, a research manager at the Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative (DNDi), explained that Chagas is neglected partly because “it’s a silent disease that stays hidden for so long in your body … because of the asymptomatic nature of the initial part of the infection.”
Referencing the poor populations, Forsyth continued, “The people affected just don’t have the power to influence healthcare policy. There’s this confluence of biological and social issues that keep it hidden.”
But as Chagas travels to other continents, its visibility is increasing and it’s now known that it can be transmitted through blood transfusions and organ transplants, and from mother to baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Professor David Moore, a consultant at the Hospital for Tropical Diseases in London, created the Chagas Hub, a UK-based facility with the primary goal of having “more people tested and treated, and to manage the risk of transmission, which in the UK is from mother to child,” he said.
Moore said that progress in eliminating Chagas is “glacial,” and addressing the target set by WHO for a 2030 disease elimination, he said, “I can’t imagine that we’ll be remotely close by 2030. That seems highly unlikely.”
Chagas can be treated with two medicines, benznidazole and nifurtimox, both on the market 50 plus years, that Moore says is “toxic, unpleasant, not particularly effective.”
It can cure a baby but there’s no guarantee the medications can prevent or curb disease progression in adults.

As for severe side effects, Rodríguez remembers coming out in hives, feeling dizzy and nauseated. She completed treatment and goes for check-ups every year.
Moore adds that more effective medication for Chagas is critical in curbing its spread but right now, there’s no financial appeal to pharmaceutical companies.
Until there’s a higher market appeal to develop more treatments, Hernández is on a mission to make the silent disease louder, in her title as president of the International Federation of Associations of People Affected by Chagas Disease (FINDECHAGAS).